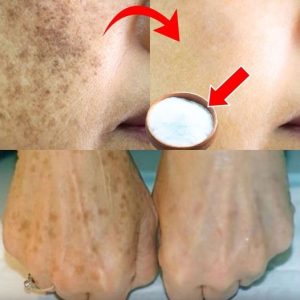
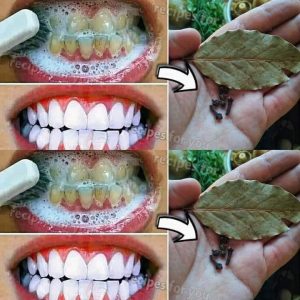
Ginger is widely celebrated for its numerous health benefits, from easing nausea to reducing inflammation. However, like all things, it’s not suitable for everyone. There are certain conditions where consuming ginger can do more harm than good. If you have any of the following health issues, it’s best to avoid ginger and seek alternative remedies.
Blood Disorders
1. Bleeding Disorders: Ginger has natural blood-thinning properties, which can be beneficial for heart health but problematic for those with bleeding disorders. If you have hemophilia or any other condition that affects blood clotting, consuming ginger can increase the risk of excessive bleeding.
2. Surgery: If you’re scheduled for surgery, it’s advisable to stop consuming ginger at least two weeks beforehand. Its blood-thinning effects can lead to complications during and after the procedure.
Gastrointestinal Issues
1. Acid Reflux: Ginger is known for its digestive benefits, but it can be too stimulating for those with acid reflux or GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease). The spiciness of ginger can exacerbate symptoms, leading to heartburn and discomfort.
2. Gallstones: Ginger stimulates bile production, which is usually beneficial for digestion. However, if you have gallstones, this increased bile production can cause pain and complications. It’s best to avoid ginger if you have known gallbladder issues.
Pregnancy
1. High Risk of Miscarriage: While ginger is often recommended for morning sickness, it should be consumed with caution during pregnancy. In large amounts, ginger can increase the risk of miscarriage, especially in the first trimester. Always consult your doctor before using ginger as a remedy when pregnant.
2. Late Pregnancy: During the later stages of pregnancy, ginger can sometimes cause contractions. If you are nearing your due date, it’s wise to avoid ginger to prevent premature labor.
Heart Conditions
1. Heart Medication Interactions: Ginger can interact with certain heart medications, particularly those for blood pressure and blood thinners. This can lead to adverse effects such as irregular heartbeat or dangerously low blood pressure. Consult your healthcare provider if you’re on heart medication and considering ginger.
Diabetes
1. Blood Sugar Levels: Ginger can help lower blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for many. However, for those on diabetes medication, this effect can sometimes lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Monitor your blood sugar levels closely if you consume ginger and have diabetes.
Conclusion
While ginger is a powerful natural remedy with many benefits, it’s important to be aware of its potential risks for certain health conditions. If you have any of the issues mentioned above, it’s best to avoid ginger and consult with a healthcare provider for alternative treatments. Staying informed and cautious can help you enjoy the benefits of natural remedies safely.